Pancreatitis in children: from symptoms to treatment
Pediatric pancreatitis is a fairly common diagnosis, especially among children with certain digestive problems. The disease can be extremely dangerous if the child fails to receive proper treatment in a timely manner, and therefore the task of not only doctors, but also parents, is early detection of the pathology.
About the disease
About the presence of the pancreas in our body, we often begin to guess only when it suddenly "fails". Childhood pancreatitis, which often begins without symptoms or “masks” skillfully as a variety of diseases of the digestive tract, is no exception.
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the pancreas. It is located next to the stomach. The stomach takes in food, in it it goes through the primary breakdown, after which the food mass enters the small intestine, and this is where digestive enzymes are needed, which, in addition to insulin, are produced by the pancreas. She gives her secretion product to the duodenum. But this is how a healthy gland works.
In the inflamed pancreatic enzymes are produced normally, but they are activated earlier than they go where they are needed for proper digestion. This only enhances the inflammatory process, as iron, in fact, begins to digest itself. Gradually, the gland tissues are damaged, they are worse at coping with their enzyme production task, and enzyme deficiency develops. In severe cases, necrotic changes in the gland begin - pancreatonecrosis, in which the predictions are very disappointing. In many cases, it ends in death.
Pancreatitis occurs in children in approximately 15-25% of cases, if we take the group susceptible to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as a basis.
Very often, incipient pancreatitis goes unnoticed. Parents treat completely different diseases, the symptoms resembling inflammation of the pancreas, for example, dysbiosis or gastritis.
Classification and species
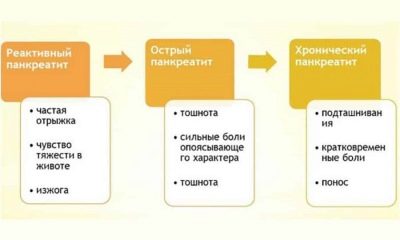
Doctors to determine the type of pancreatitis use different systems of classifications. The very first appeared in the middle of the last century, but it attributed the inflammation of the pancreas only to alcoholics. When it became clear that both children and adults who do not drink alcohol suffer from the disease, a universal classification was created, which in 2007 was supplemented by German scientists.
Thus, today all cases of inflammation of the pancreas are divided into:
- acute pancreatitis;
- recurrent acute;
- chronic;
- chronic in the acute stage.
In order to better understand the essence of this separation, one should know that the process that has just emerged with all its characteristic symptoms is called acute. If the disease recurs even before half a year has passed from the moment of acute pancreatitis, they speak of a recurrent acute illness. If more than half a year has passed, doctors diagnose “chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage”.
Depending on how affected the pancreas is, if destructive processes have begun in its tissues, determine:
- edematous pancreatitis (gland is edematous, but only individual cells are damaged, there are no large necrotic areas);
- destructive (there are necrotic foci).
Specifying a condition, doctors specify, the small, average or large centers of a necrosis are present.It is noteworthy that doctors usually do not use the term “pancreatonecrosis”. They are mainly operated by pathologists to describe the causes of death.
In the course of the disease there are several phases:
- enzymatic stage - lasts up to 4-5 days;
- reactive period - starts at 5-6 days and ends at 14 days;
- sequestration - starts from the 15th day of the onset of the disease;
- stage of outcome - Lasts about six months after the onset of the disease.
Children's pancreatitis, if it is acute, is usually accompanied by inflammation and swelling of the gland. In the most severe cases, hemorrhagic symptoms occur - hemorrhage. But in childhood acute pancreatitis in its pure form is very rare. In 90% of cases in children, a chronic disease is recorded, and often it is hidden.
The peculiarity of childhood imposes an imprint on the diagnosis: If a baby is diagnosed with reactive pancreatitis, then doctors regard it as a pancreatic response to a variety of pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, and such a disease is reversible with proper and timely treatment.
If untreated, reactive pancreatitis for children can turn into a true one, in which it begins to destroy the tissues of the gland.
The reasons
The pancreas of a child can react with inflammation and swelling to many unfavorable factors, but then its own enzymes, which begin to activate ahead of time right in the gland, become the cause of the intensification of the inflammatory process. At the same time, not only the glandular tissues, but also the entire body, suffer, because decay tissue cells begin to enter the bloodstream, and this is precisely the reason for intoxication in the acute form of the disease. This may be pancreatitis with salmonellosis and or acute herpes virus infection, with enterovirus (intestinal infection).
Parents do not always attach importance to the symptoms of acute pancreatitis, and then the disease can turn into chronic. Exacerbations will occur when a variety of situations and factors affect the children's body:
- food poisoning;
- any viral disease;
- fungal infections;
- food allergies;
- overeating or malnutrition;
- stress, anxiety.
It is believed that the main cause of the inflammatory process in the gland is a violation of the outflow of secretions that it produces. Excretory ducts may begin to cope worse with their functions after blunt abdominal trauma, against the background of parasitic diseases in children (especially with opisthorchiasis and the presence of ascaris), in the presence of various diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, gastroduodenitis, hepatitis, gallbladder disease).
The gland can begin to produce an excess amount of enzymes that simply cannot be completely eliminated into the duodenum, in such cases:
- the child eats improperly - there is a lot of fatty, spicy, chips, fast food, drinks a lot of soda, eats irregularly, overeats;
- the child suffered severe poisoning;
- the baby is allergic to foods or medicines (corticosteroid hormones, antibiotics, sulfonamides, cytotoxic drugs, some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are especially dangerous for the infant's pancreatic pancreas);
- the child is diagnosed with obesity;
- There is a confirmed excess function of the thyroid gland.
Often, pancreatitis develops in children who have had mumps (mumps) and dysentery.
Signs of
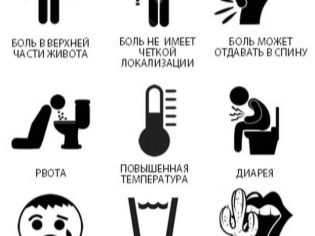
An acute attack of pancreatitis can be recognized by severe pain in the stomach. It develops suddenly and delivers quite pronounced inconvenience. Children at a conscious age (5-6 years, 7-8 years and older) may well describe their feelings and indicate exactly where it hurts. In infants the attack of pain is manifested a strong cry and pushing the legs to the stomach, in connection with which mothers often confuse inflammation of the pancreas with intestinal colic.
The pain in a child is concentrated mainly in the upper abdomenmany complain that slightly "gives" to the right side of the body. Acute attack peculiar to vomiting in her parents can easily distinguish bile impurities. After a seizure, there is no such relief. starts to feel sick again. Often the temperature rises.
It is important to pay attention to the color of urine and feces. If the head of the pancreas becomes inflamed and increases in size, the child may develop mechanical yellow - the outflow of bile is disturbed, in connection with which its coloring pigments enter the blood. The skin becomes whiteish, the whites of the eyes, the urine is colored dark, and the stool, on the contrary, becomes light, almost white.
When the signs of acute pancreatitis are described, it is important to call an ambulance. But in most cases, children's pancreatitis occurs in milder forms, and age also plays a role: the younger the child, the less visible signs of pancreatic disease may be.
Attention should be paid to symptoms such as flatulence, bloating, repeated nausea and vomiting, loose stools, loss of appetite. Temperature is usually within 37.0 degrees and a little higher baby looks pale, dry mouth.
Chronic pancreatic disease is sharply accompanied severe pain attacks. From time to time the child usually complains of aching pains in the stomach that may increase, if on the eve of the baby ate something fat or drank a soda, as well as during periods of emotional and psychological stress, strong physical exertion. Such aching attacks are also short - from an hour, and long - up to several days.
Children with a chronic pathological process in the pancreas are prone to heartburn, have reduced appetite, often experience nausea, especially after eating, often suffer from unstable defecation - constipations are replaced by diarrhea and vice versa.
Symptoms of complications may gradually develop - the child begins to lose weight, he develops pleurisy or diabetes.
How to diagnose?
Self-diagnosis is not worth doing. If the signs described above appear, it is worth visiting a doctor to undergo a detailed examination. The doctor will be able to suspect the signs of pancreatitis in a child when palpating the epigastric region, especially if the pancreas is swollen and enlarged. But the diagnosis is made not only by a combination of symptoms and manual research. An important role is played by laboratory diagnostics.
If a child has acute pancreatitis, then a large number of leukocytes is found in the blood, high ESR values. A more accurate information is given by a biochemical blood test - it can determine the increased activity of pancreatic enzymes, as well as a high content of glucose in the blood serum. The presence of certain pancreatic enzymes is also determined in the feces.
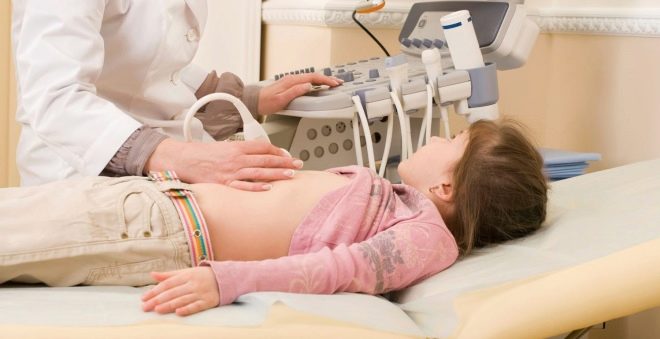
The child does an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, stomach, gallbladder. Ultrasound provides an opportunity to see whether the gland is enlarged, whether there is swelling, a change in its shape, or areas of necrotic lesion. If necessary, computed tomography of the abdominal organs or MRI may be recommended.
After going to the doctor with characteristic complaints, it is very important that he could get as much laboratory and instrumental information as possible to distinguish pancreatitis from stomach ulcers, acute cholecystitis, renal colic, intestinal obstruction, and appendicitis.
How to treat?
How to treat acute or chronic pancreatitis, depends on how large the lesions of the gland are, whether there are complications. In any case, both in acute illness and in exacerbation of the chronic, it is important to create conditions so that the gland is in functional rest, that is, therapeutic fasting is prescribed for several days, until the attack retreats.
Acute pancreatitis requires that the child be in the hospital (up to 3-4 years old - along with the parent). Baby is recommended bed rest and the lack of food, you can not feed anything. You can drink mineral water, the composition of which is alkaline. The child is administered a glucose solution, hemodez, enzyme preparations. After 2-3 days, a therapeutic diet is prescribed, in which the pancreas will not produce too much enzymes.
Such food implies complete ban on fatty and fried dishes, on concentrated meat broths, pork, lard, offal, all smoked, sausages and sausages, oily fish, canned, pickled, sauces, eggs, seasonings, raw onions, garlic, beans, spinach, bananas , pomegranate, grapes, sweets, cocoa and fizzy drinks, sweet pastries. The child’s menu resembles a gastritis menu; it includes vegetable stews, mashed potatoes, mashed potatoes, vegetable soups, boiled and baked meat, poultry, fish. Among mineral waters, preference is given to "Yessentuki" (No. 4, 177) and "Narzan".
If a child has chronic pancreatitis, anesthesia is considered the main tactic in treatment. Further, it is important to plan the child's nutrition so that repeated exacerbations are excluded.
At the time of rehabilitation after the attack, the doctor may prescribe drugs. pancreatic enzymes (Pancreatin, Creon) - these drugs will contribute to the digestive processes, while slightly loading the pancreas itself. It is important to monitor the mode of the day, nutrition. Treatment is possible at home.
The exact list of drugs that a doctor can prescribe to a small patient will only be reported by the doctor himself after the examination, because other medicines are also given to eliminate the associated symptoms and pathologies: antibiotics, hormonal drugs, and antispasmodics are used. The regimen is also individual.
In severe cases, when conservative treatment does not help, and destructive changes in the gland are progressing, according to the clinical recommendations, surgical treatment can be performed - resection of the gland, necrotomy, removal and drainage of a gland abscess.
Forecasts
Many scientists have devoted their monographs to pancreatitis, but even in them you will not find an abundance of information about prediction - this is a very individual disease. In general, it can be noted that mild forms of acute reactive pancreatitis in children have quite favorable projectionsif, of course, parents and doctors immediately provided the child with the necessary help and treatment. Slightly worse than the prognosis for hemorrhagic and purulent form of the disease. With pancreatic necrosis, the probability of death is high.
In the chronic form of childhood pancreatic disease, it is difficult to make predictions - it all depends on how often and how much the disease is exacerbated.
If a child eats properly, leads a healthy lifestyle, regularly undergoes preventive treatment to prevent relapse, receives the necessary spa treatment he needs, then the predictions are also evaluated as quite favorable.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky argues that pancreatitis is a disease of a wrong lifestyle, and it is always easier to prevent than to cure it (if it is not a hereditary form of the disease). For the prevention of this disease, the doctor suggests a number of measures.
- Do not overfeed the child, do not force him to eat up everything to the crumbs - this is where the wrong eating habits begin to form.
- Carefully ensure that the products on the table of the child are thermally treated fairly well so that they have a valid shelf life.
- From an early age teach your child to mobility and activity. Lying down lifestyle, laziness and constant viewing of cartoons in combination with chips or hamburgers can lead to obesity of internal organs, including the pancreas.
- Teach your child to eat healthy food, if he does not like it (which is not at all uncommon), change the food, arrange and serve dishes differently, so that they are more attractive. A hungry child will eat what is offered - this is the golden rule.
- Harden and rejuvenate your baby, walk more in the air, use wiping and cool baths.
It is not necessary for any reason to give the child pills (from the head, from the priests, from the rash, and so on). Uncontrolled and excessive medication is one of the main causes of childhood pancreatitis.
Reviews
According to parents, in the treatment of pancreatitis in a child the most difficult thing is to maintain the diet recommended by doctors. With a food pause, if the food is not recommended at all, after the attack, the child begins to ask to eat the next morning, and then the iron will is required from the parents. In some cases, if children are over 3 years old, doctors are allowed to drink a small amount of water with honey.
When treating chronic pancreatitis, mothers often acknowledge that it is not possible to withstand the recommended diet for a long time. Anyway there are breakdowns (on holidays, for example). Most argue that It is these breakdowns that lead to the onset of pain and discomfort, diarrhea, but after the resumption of proper nutrition, everything goes away. As a rule, as experienced parents say, after a few years of a proper diet, foods that were previously banned can be gradually added to a child’s diet in small portions. With a reasonable introduction, the child’s condition does not suffer.
About pancreatitis in children, see the following video.