When do cesarean section?
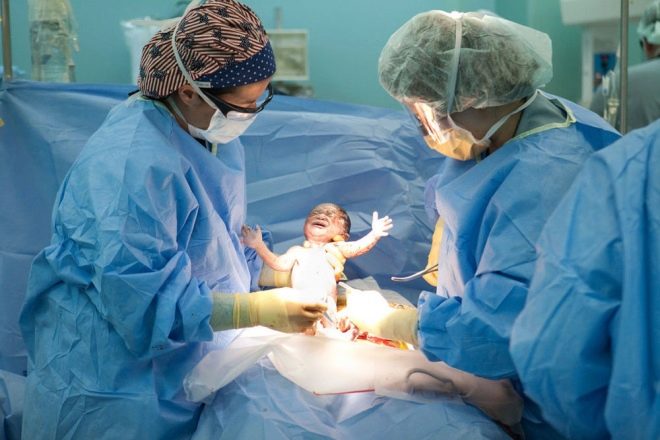
A cesarean section is a curative surgery, in which the child and the placenta are removed from the mother's womb not through the genital tract, as provided for by nature, but through incisions in the abdominal wall and uterus made by the surgeon.
Such an operation can be scheduled in advance, and can be appointed on an emergency basis to save the life of the mother and baby. Each case has its own indications for operative delivery. In this article we will tell you when a surgical obstetric aid is recommended for a woman.
Plan
Since a cesarean section is considered a complex operation, it is not recommended. After it, certain complications are possible, the intervention itself is not considered natural and is a strong stress for both the mother’s body and the body of the newborn.
That is why the Ministry of Health of Russia recommends surgical surgery only in certain situations in which physiological labor is either impossible or extremely dangerous. The list of these testimonies is provided by an internal document - a letter from the Ministry of Health dated May 6, 2014 No. 15-4 / 10 / 2-3190.
The list of these indications is recommended for work by doctors of all specialties in our country, since sometimes such a decision must be made urgently, urgently, even if there is no obstetrician-gynecologist nearby. Therefore, the technique of operative labor is also taught to doctors of any specialization.
The number of operative labor in the proportion of childbirth in general is growing in all countries. Russia is no exception. Today, according to statistics, every fifth little Russian is born surgically. Experts tend to believe that expanding the list of indications for such an operation is an inevitable requirement of time. Today, the number of women giving birth for the first time after 36 years has increased dramatically. IVF has also become popular and widespread, some couples come to give birth to second and third IVF babies.
Women who had previously given birth surgically come for the second, third, and fourth child. Also expanded the indications for surgery, which doctors say that they exist in the interests of the fetus.
The decision about a planned operation is usually made by 33-35 weeks of gestation, when a full history of the doctor, observing the pregnant woman, is available.
The reasons for the appointment of planned surgical delivery, as recommended by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, are as follows.
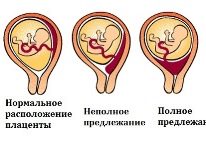
- The placenta is low, it completely overlaps the internal pharynx or enters it partially, but there are signs of detachment or the likelihood of bleeding. Independent labor in the complete and complete presentation of the "children's place" is impossible, and the partial presentation of the placenta is dangerous with the occurrence of massive bleeding during labor, which can lead to the death of the woman and the baby.
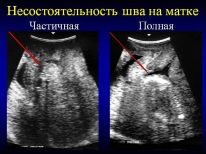
- Failure of the uterine scar from the former cesarean section, from myoectomy, excision of the angle of the reproductive organ after ectopic pregnancy, etc. The scar is considered to be unhealthy heterogeneous, thin, with "niches". Such a scar does not allow for independent delivery due to the risk of uterine rupture, even if the woman has a history of a single cesarean section.
- Placental abruption before term. Neither the location of the placenta in this situation, nor its presentation of the role do not play.The more detachment, the stronger the oxygen starvation of the fetus. With complete detachment, the baby rather quickly dies. Therefore, a cesarean section is a saving measure.
- Scars on the uterus from any operations, as well as two or more caesarean sections in history. Such a pregnancy cannot be delivered naturally.
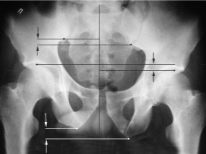
- Mechanical obstacles to the normal physiological birth of the baby. Such obstacles include a narrow pelvis (second degree and above), deformities of the pelvic bones, joints, existing in a girl from birth or acquired as a result of injuries, tumors in the uterus, on the ovaries, tumor formations of other pelvic organs, groups of polyps.
- Symphysitis (sprawling of the bones of the symphysis).
- Incorrect location of the fetus in the uterus (pelvic, transverse or oblique, buttock-foot presentation), especially if the baby is among the heroes and the estimated weight of the crumbs exceeds 3.6 kg.
- Multiple pregnancy, if one of the two babies is located in the uterus in an irregular position or with pelvic presentation of their babies, who are located first to the exit.
- The failure of the cervix and vagina. This refers to ruptures of the perineum after the first birth (third degree), as well as the pathological narrowing of the birth canal, the presence of scars on the cervix after erosion treatment in those who have not given birth or after difficult births have given birth.
- Multiple pregnancies by identical twins, if both children are inside the same sac.
- Multiple (often singleton) pregnancy after IVF.
- Delay in the development of the third degree fetus - the baby simply may not have enough strength for independent birth, because childbirth is difficult not only for the mother, but also for the child.
- Prolonged pregnancy - at 42 weeks gestation. The operation is carried out only if other methods and methods of stimulation of labor in a woman in the hospital did not have the desired effect.
- The state of severe gestosis in women (with edema, large weight gain, signs of increased blood pressure).
- A complete ban on attempts for the mother. It is strictly forbidden to push for a progressive myopia with a retinal detachment in history, as well as for a number of ailments of the cardiovascular system, in the presence of a transplanted donor kidney, etc.).
- Hypoxia of the fetus, confirmed by the results of CTG, ultrasound, USDG, when the condition of the child is regarded as threatening.
- Umbilical cord prolapse.
- Rash on the genitals, the presence of genital herpes of the primary type - there is a possibility of severe infection of the fetus during its passage through the birth canal.
- The presence of HIV infection in a woman, if during the period of childbearing, she did not receive maintenance therapy for a number of reasons.
- Blood clotting disorders in a woman and her child.
- Malformations of the baby - omphalocele, gastroschisis and others.
Individually, a planned operation can be recommended in the event that the woman was injured during the first childbirth, died, became disabled. Fear of childbirth in such women is almost pathological in nature, and therefore it will be safer for everyone if the probability of birth trauma is minimized.
Extra
Unplanned delivery operation is usually performed already at birth or in situations that have arisen urgently even during pregnancy. The reasons for the emergency operation can be any, but the goal is always the same - saving the lives of a woman and a baby. The Ministry of Health provides such vital indications for which a cesarean is made urgently:
- premature rupture of water in the absence of labor activity and the effect of its stimulation;
- any bleeding associated with impaired phytoplacental blood flow;
- premature detachment of the placenta;
- signs of the beginning of uterine rupture along the rumen line or the beginning of a rupture;
- weakness of generic forces in the stage of contractions, if the stimulation was ineffective, weakness of attempts, in which even against the background of the complete opening of the neck, no fetus is born;
- acute state of oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- death of the pregnant woman or agony if the baby is alive (to save the baby’s life).
Emergency operations are more likely to have complications arising both in the process of surgical intervention and in the postpartum period.
If a woman has one or more indications for surgical delivery (indicators can be combined differently), it is considered more correct and safe to prescribe a planned cesarean section, since the probability of complications after it is lower.
Is it possible to choose at will?
Recently, the so-called elective caesarean section is gaining popularity in the world, in which a woman is given surgical births at her own will. There may not be indications from the doctors for the operation, but the woman deliberately chooses the surgical delivery. The reasons may be different - the fear of pain in childbirth, the negative experience of the first birth, the pathological fear for the health of the child, etc.
In Russia, in state maternity hospitals and perinatal centers that provide services under the compulsory health insurance program (for a policy), an elective caesarean section is not done.
From the point of view of bioethics, the doctor cannot harm the patient, and surgery without a reason is a clear harm to her health.
At their own request in our country, caesarean can be done only in some private and necessarily paid clinics. The cost of elective caesarean section is within half a million rubles.
Caesarean section is prescribed for a reason. There is always a good reason, which covers the possible complications and harm of surgical intervention. This must be remembered by women who are not shown to have a delivery operation as such, but they really want the birth to go that way. When making a decision, you need to be well aware that a scar on the uterus can complicate subsequent pregnancies and childbirth, and even lead to infertility.
In addition, purulent and severe infectious complications after surgery, violation of the integrity of the bladder, mechanical injury to the intestinal wall, ureters during manipulations, mechanical injury to the uterine wall, the occurrence of severe bleeding in the operative and early postoperative periods are not excluded.
Preparations for anesthesia affect not only the mother, eliminating pain and sensitivity, but also the child. This should not be forgotten when choosing a mode of delivery.
About indications for surgical childbirth experts tell in the next video.