Symptoms and treatment of adhesions after cesarean section
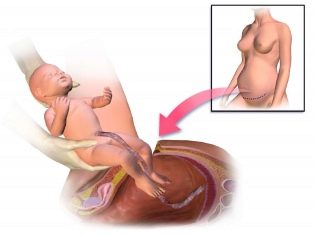
Adhesions after cesarean section is an unpleasant complication that occurs already in the postpartum period. The main cause of adhesive disease is the operation itself, that is, surgery, which launched the pathological processes. In this article we will talk about why and how adhesions appear and how to treat them.
What it is?
What women call adhesions, in medicine, has a more global name - adhesive disease. It is directly related to the penetration of the surgeon into the abdominal cavity. Any penetration there is unnatural from the point of view of nature, and therefore the human body can activate defense mechanisms.
As a rule, when the body begins to defend itself, it does not become easier for a person to do so. Thus, when bacteria and viruses enter the respiratory tract, coughing begins, and if foreign protein enters the body, an allergy occurs. Adhesions are also a defense mechanism, but it starts when there is a risk of infection inside the abdominal cavity.
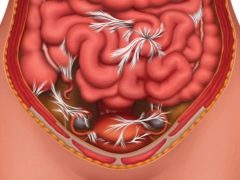
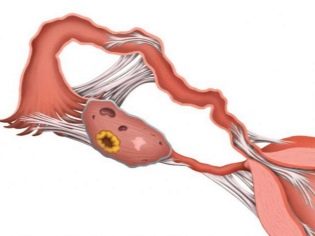
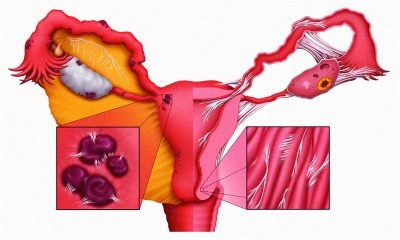
Any operation, and cesarean section is no exception, carries with it the risk of infection. The body of a woman, intending to protect the healthy organs of the abdominal cavity from injured during the operation, contributes to the appearance of a large amount of connective tissue. As a result, weights that can tightly glue adjacent organs and their separate structures with connective tissue develop. These tyazh and are spikes.
Heavy duty is not conducive to normal life. They squeeze the organs, interfere with them, disrupt their functioning. Sometimes the adhesions after cesarean section can cause secondary infertility if the adhesions, ovaries, appendages are drawn into the adhesions. It is possible the development of intestinal obstruction, if strands spread to the intestines.
Development mechanism
The protective mechanism, which leads to the formation of unnecessary and unpleasant adhesions, is very complex and multistage. All organs inside the abdominal cavity are covered with a very thin layer of the so-called peritoneum leaves. They give the organs smoothness and also produce a small amount of fluid, which makes it possible to move and slide the organs in the abdomen when the body position is relative to each other.
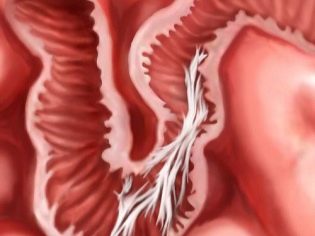
After surgery, there is a slight swelling around the damaged tissue. It causes precipitation of fibrin on the leaves of the peritoneum. The role of fibrin is great: it helps heal wounds due to its stickiness. But in this case, it simply glues the neighboring organs together. After the formation of fibrin on the internal organs, it takes about three days until the formation of special cells in it. Fibroblasts begin to produce collagen. Connective tissue is formed about a week after the operation, and three weeks after cesarean section, the final formation of adhesions is completed.
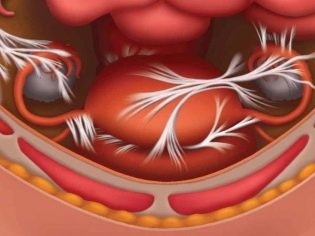
More others are at risk of the formation of adhesions after surgical labor of a woman, who have a history of diseases of internal organs, as well as puerperas, who have undergone surgery with complications or have developed in the early postoperative period. Fusion can be observed on the uterine stitch, on the reproductive organs, bladder, intestines, ureters.
Symptoms
It is rather difficult to determine the adhesions for any one specific group of symptoms, since the symptoms themselves are dependent on where the adhesions were formed, how common they are, the functioning of which internal organs they violated. It so happens that a woman may not feel anything unusual for a long time, and only then the illness will manifest itself acutely, suddenly and immediately require hospitalization and medical assistance.
The most common group of symptoms is intestinal. A woman may feel abdominal pain, nausea, sometimes vomiting occurs, the temperature rises. When trying to press on the stomach with your fingers, a sharp sharp attack of pain occurs. At the same time, the newly-made mother herself does not really understand where exactly the pain is located - it seems to her that it hurts everywhere.
Quite often, adhesions appear persistent and systematic diarrhea or constipation. A woman can fall pressure, appear weakness.
Not always signs of adhesions are permanent. Quite often, the disease manifests itself, and then subsides. In this case, doctors talk about the development of chronic adhesive disease. It can last for years.
If the reproductive organs are involved in adhesions, the illness is manifested by menstrual disorders, pain during menstruation, more intense than before birth.
If these symptoms do not occur, it is possible the hidden course, and then a woman can learn about it from the gynecologist, whom she will turn to only when attempts to conceive the next child will be fruitless. Postoperative adhesions are a common cause of female secondary infertility.
How to detect?
An experienced surgeon, knowing that a woman had previously undergone a caesarean section, will suspect adhesions in the first place when there are characteristic complaints. The complex of diagnostic measures in this case will be quite extensive. The woman will be given an ultrasound scan, CT scan of the abdominal cavity, radiographic examination with contrast, electrogastroenterography.
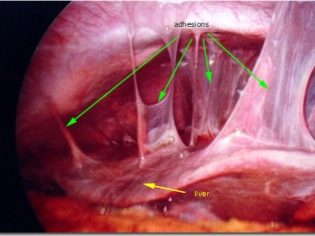
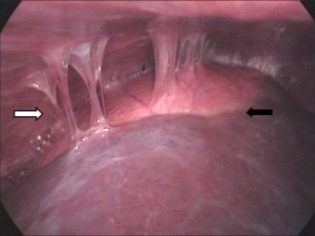
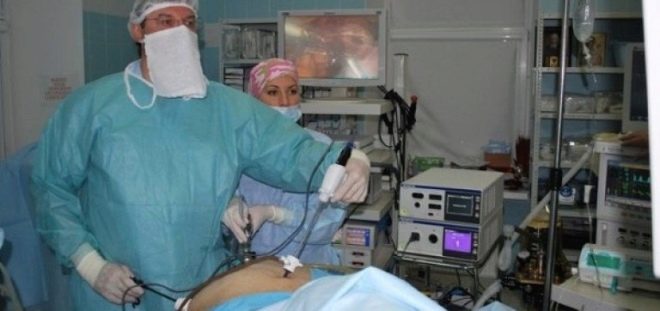
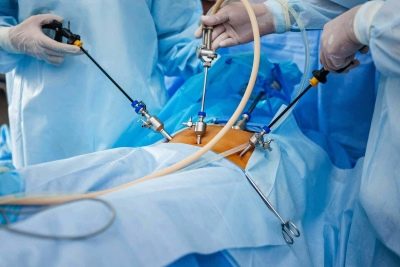
The control study is diagnostic laparoscopy, it allows you to determine with great accuracy the place and nature of the lesion by adhesions. At the same time with this diagnostic, it is possible to cure the disease - to eliminate adhesions by laparoscopic method.
Treatment
It is possible to treat adhesions formed after surgical delivery in two ways: conservative and surgical. The first method aims to relieve symptoms, to eliminate the influence of cords on the work of internal organs. If conservative methods are unsuccessful or an acute adhesive disease attack, an urgent surgical intervention is prescribed.
Conservative treatment includes the elimination of factors that contribute to the appearance of pain. For constipation, an enema is administered, women are prescribed medications to reduce gas formation, laxatives, and a special diet that will include a large amount of food rich in coarse fiber: raw vegetables and fruits.
It should be noted that even minor deviations from the recommended diet by the doctor during adhesions may well cause a new painful attack.
Complex physiotherapy is also considered to be quite effective, especially methods such as paraffin baths, iontophoresis, mud therapy.
A woman with adhesions will have to give up visiting the gym - physical exertion should be strictly metered and feasible. Excessive tension of the abdominal muscles can lead to a new attack. Swimming is allowed, but in a special medical medical group under the supervision of a physician.
If a woman is tormented by belching, vomiting, she will be prescribed medications for nausea. If vomiting has been repeated, rehydration therapy is additionally carried out to eliminate the signs of dehydration.
Surgical removal of adhesions is a technically rather complicated process. It may require painstaking and detailed preparation. If a woman with acute pain was taken to the hospital, the preparatory stage is reduced to a minimum, but this does not cease to be completely full, as many patients think.
The preparation is mainly medical in nature: a donor plasma is transferred to a woman before the operation, sodium chloride and Ringer-Locke solution are injected to eliminate any signs of possible dehydration. At the same time, the composition of the blood is normalized. It also shows the introduction of drugs that will help the process of detoxification, reopolyglukine with hydrocortisone.
At the time of the operation, which is carried out under general anesthesia, the scar on the uterus is not touched or excised: such an intervention may cause additional complications. Spikes neatly disconnect, push apart. If a necrotic area is found on the affected organ, a partial resection is performed.
If adhesions are observed on the organs of the reproductive system, laparoscopic removal is quite often prescribed, and adhesions in the uterus can also be removed during hysteroscopy.
Unfortunately, despite the fact that the methods look quite solid and the medicine has modern equipment, trained by surgeons, the likelihood of re-formation of adhesions is rather high.
According to WHO, it is estimated at 17–20%. This means that every fifth woman with adhesive disease after cesarean will have no surgery to eliminate adhesions - strands will form again.
Forecasts
If adhesions after surgical labor have been sporadic, medical prognoses are usually favorable. However, multiple cords that significantly disrupt the functioning of internal organs can be very dangerous.
The first prevention of adhesions will be taken by surgeons who make a woman a cesarean section. During the operation, they will comply with the basic requirements: use only suitable and safe suture materials, do not violate the suturing technique, do everything possible to reduce the risk of infection.
In the early postoperative period, in order to avoid the development of adhesions, it is recommended that a woman not stay for a long time. After 10 hours you can get up and walk. Moderate and adequate movement is a guarantee that adhesions are not formed, even if a certain amount of fibrin is formed on the peritoneum.
After discharge, the woman should also walk more, not to strain the abdominal muscles, until half a year has passed since the operation. It is important at any stage after surgical delivery to prevent constipation, to eat correctly and efficiently. It is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the doctor: do not lift weights, do not return to intimate life, until at least 2 months after delivery. Violation of these requirements is fraught with the possibility of damage to internal and external sutures, infection of postoperative wounds, which, in turn, may cause a little later development of adhesions.
When the first symptoms appear, a woman should definitely see a doctor, because adhesive disease in a chronic, neglected form can be not only dangerous, but also very difficult to cure.
Considering that the symptoms are not always obvious, the woman needs to periodically visit the gynecologist and the therapist, to be attentive to her well-being. If menstruation changed its character after CS, if intestinal symptoms began to appear regularly, it is worthwhile to suspect spikes and inform the doctor about it.
Effective exercises in the treatment of adhesive disease can be seen in the next video.