Features of the chair after cesarean section
After a cesarean, most women find it difficult to go to the toilet. It is not so much pain, how much scary, because you can not push. Problems with defecation, and sometimes with urination, occur in about 75% of newly-minted moms, whose births took place in the operating room. In this article we will talk about why such delicate problems arise and how to cope with them.
Causes of pain
During the surgical labor, the abdominal muscles are injured. It takes time to restore them, and therefore in the first days after a cesarean, it is so painful for a woman to walk “big”, because to perform an act of defecation, you need to strain certain abdominal muscles.
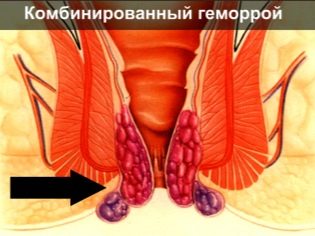
Sometimes problems are aggravated by the development of postpartum hemorrhoids, which can manifest not only after physiological birth, but also after cesarean, because it is not a consequence of the fact that during labor the woman had to push, but is directly due to pregnancy when the lower veins, including hemorrhoidal, suffered from circulatory disorders and pressure of a heavy uterus.
All women after surgery to scare. The fear that the stitches will break up, and the fear of pain in the injured peritoneum becomes a formidable obstacle in the task of normalizing the stool. And the task is extremely important. The fact is that overfilled with constipation or irritated intestines with liquid stool can adversely affect the healing of internal sutures in the uterus, the contraction of the uterus to its former size.
After the operation, in no case should the intestinal overflow or swelling be allowed, so a woman should undergo a cleansing enema before surgery, and after the operation a strict diet is prescribed for two days.
Fear is the main cause of impaired stool after surgery. At the psychosomatic level, the fear of possible pain and a violation of the stitches causes a spasm of the anal sphincter. As a result, it is impossible to go to the toilet for a great need.
The reasons
Constipation - a real scourge of women after operative delivery. Some fail to cope with this problem until the end not only in the first days and weeks after surgery, but also in 2-3 months. Causes of constipation lie not only in psychological fear.
Often the reason lies in the temporary physiological paresis of the intestine. It just stops shrinking. This occurs as a response to surgery in the abdominal cavity. By the way, in the same way the intestine can react to any other operation in this part of the body. Most often paresis develops after suffering general anesthesia.
In addition to difficulties with defecation, there are practically no other signs of intestinal function - gases do not leave, from time to time a woman experiences spastic pain, the stomach asymmetrically distended. If pathology is detected in the first three days after operative delivery, there is no reason for anxiety, but if the problem persists longer, you should consult a doctor.
The cause of constipation and pain during bowel movements can be spikes. At the same time, some parts of the internal organs are “soldered” with each other with thin films. So the human body is trying to protect itself against the spread of infections after gross outside intervention.
If adhesions are observed in the area of bowel loops, problems with the chair are unavoidable. May require surgical assistance in the dissection of adhesions.
The muscles of the peritoneum are stretched and relaxed after carrying a baby. Inside the abdominal cavity does not create the necessary pressure to push the fecal masses. And this is another very common cause of constipation after surgery.
In addition, the intestine is "lazy" - it was artificially cleansed before the operation, then the woman almost did not eat anything, following a restrictive diet. If it is still constantly lying, moving a little, then bowel motility will be minimized.
To combat constipation after surgery on the third day, the doctor prescribes another enema, if before that time the woman could not go to the toilet on her own. An alternative to the unpleasant procedure of washing the intestines can be candles with a laxative effect, allowed during breastfeeding, microclysters.
The danger of diarrhea is also not underestimated. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration of the female body, especially since not so long ago there was a lot of blood loss, and the release of postpartum lohia is still ongoing. Diarrhea can negatively affect the production of breast milk.
Liquid stools in the first days after surgery are rare. Most often, this intestinal disorder "starts" after discharge home. The cause may be dysbiosis. The balance of intestinal flora is disturbed in puerperas who have been given antibiotic therapy for the prevention of postoperative complications.
The reason may be a violation of intestinal motility, poor diet, psychological state - with postpartum depression and depression in women almost always disrupts the intestine.
The immunity of women who have undergone surgery is significantly reduced, and therefore it is possible that diarrhea is a manifestation of an intestinal infection. If diarrhea lasts for more than a day, it is advisable to consult a doctor, especially since all antidiarrheal drugs are contraindicated in women who breastfeed the baby.
Rice water will help, normalization of nutrition, especially its regime - food should be taken regularly, without skipping any dinners or dinners, food should be fresh.
In dysbacteriosis, the doctor may prescribe probiotics, although their effectiveness is in great doubt. Recent studies by scientists have shown that probiotics are a dummy, and they have little effect on the work of the intestines.
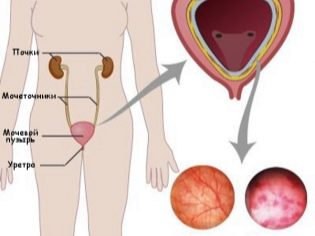
Urination problems
Pain and pain when going to the toilet "in a small way" can appear both in the first days after the operation, and after discharge. The reason may lie in the mechanical injury of the bladder during surgery (this happens infrequently, but sometimes it happens). Much more often, the cause of urinary trouble is a decrease in immunity, common to all people after surgery.
Weak immunity cannot adequately repel pathogenic bacteria, and therefore cystitis appears.
Cystitis can also be a reaction of the urinary tract to the introduction of a catheter, which is mandatory at the time of the operation and in the early postoperative period, when the puerperal cannot yet get up and go to the toilet on her own.
If a woman has previously had problems with the kidneys, urinary tract, then after surgery due to reduced immune protection, they can worsen, which also manifests a characteristic clinical picture - pain during urination, change in urine color, quantity, edema, pain in the abdomen and lower back.
Most of these complications require medical advice and the initiation of antibiotic use. But first you need to do a general urine test to know exactly in which part of the urinary system inflammation occurred.
Prevention
Since intestinal problems after surgery are ubiquitous and familiar, the doctors immediately warn the patient that they need to get out of bed after the surgery as soon as possible. No need to be afraid of pain, you need to move adequately to eliminate such unpleasant complications as the formation of adhesions, intestinal paresis, its excessive relaxation.
After 7-8 hours after cesarean, a woman can turn on her side, make circular movements with her feet, after 10 hours you can sit down and stand up. You need to walk carefully, holding the stomach with his hand. Facilitate the process of gaining physical activity can special orthopedic postpartum bandage, which will carefully support the relaxed and injured abdominal muscles.
In order to adjust the work of the intestines, after surgery, new products must be introduced gradually. On the first day you can drink only water, and in the evening - a small amount of apple juice. On the second day, a woman can have chicken broth, provided that it is secondary, that is, cooked in the second water. By the evening of the second day, a small amount of mashed potatoes without butter of semi-liquid consistency is allowed. On the third day, a woman is allowed boiled and steamed vegetables, meat purees for baby food in jars, and porridge.
To a full table, adapted for nursing mothers, you can go from the fourth day after the operation.
It is important to drink enough fluids. It will be quite easy to restore the intestines, if from the first days a woman follows all medical recommendations. In the diet after discharge should be sufficiently coarse fiber, which is contained in vegetables and fruits. Sugar, thick food, a large amount of salt, food with preservatives and dyes, legumes and cabbage, which cause increased gas formation, as well as carbonated beverages after caesarean section are prohibited.
Enema and laxatives at home also do not need to be abused. With their use, the intestine becomes more "lazy" and the problem is exacerbated. Such measures are good as a one-time aid to the intestines, but unsuitable for systematic use.
Walking, moderate activity, proper nutrition will help prevent constipation and diarrhea. If you have problems with a “small need,” you should immediately consult a doctor.
For more information about the restoration of the intestine after childbirth, you will learn from the following video.