Features of emergency caesarean section
Sometimes the need for a cesarean section occurs suddenly, unexpectedly. Such an operation is called emergency, it is carried out without prior preparation, according to strict vital signs. In this article we will talk about the features of such a delivery and consider its pros and cons.
What it is?
Emergency cesarean section on the official medical language is called the rescue operation, which is carried out according to urgent indications. This means that there is no time to plan the operation and schedule additional examinations. The child and mother need an urgent delivery on which their lives depend.
Such an operation is done at any time, the main condition is the viability of the baby.
Such an operation really helps save lives, but, alas, it carries certain risks - the likelihood of complications after emergency surgical delivery is always much higher than after planned ones.
If the operation is carried out on an urgent basis, special techniques and methods for carrying it out can be chosen. The likelihood of complications for a child is also higher than for caesarean section, carried out in accordance with the planned schedule.
Indications
The need to perform an urgent operation may occur during pregnancy, as well as during natural childbirth, if insurmountable obstacles arise that interfere with normal physiological delivery. The operation may be required as indicated by the woman, and in the interests of the fetus.
In the period of carrying a child, the complications of pregnancy usually become the reason for the appointment of a planned operation. In an emergency, there may be a need for:
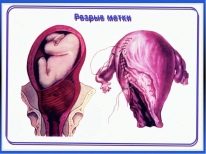
- the threat of rupture of the uterus along the old scar or the beginning of the rupture, as well as when the rupture of the uterus has occurred;
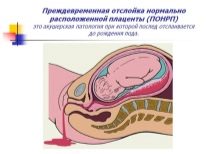
- premature detachment of a normally located placenta, as well as detachment of a low-lying “children's place” with the development of bleeding;
- sudden deterioration of the fetus - tight entanglement with umbilical cord, signs of oxygen starvation, the development of hemolytic disease due to the Rh-conflict of the mother and baby;
- sudden premature discharge of amniotic fluid, after which contractions do not develop, despite medication stimulation.
If the birth has already begun, the need for emergency caesarean section may arise at any time, especially if the woman in childbirth is at risk. The operating room is always on hand if a woman is born with a scar on the uterus (second birth after the first cesarean section), if the birth is taken in a woman who is pregnant with twins or triplets, and in other situations. Generic indicators for emergency caesarean section are:
- premature detachment of the placenta in childbirth, before the baby passes through the birth canal and is born;
- a long period after the discharge of water, if the birth does not develop;
- primary weakness of labor forces (contractions weakened, stopped, do not resume under the influence of medications or are discoordinated, the neck does not open);
- secondary weakness of labor activity (attempts weakened or stopped, the baby’s passage, the birth of its head slowed down or stopped);
- the onset of acute hypoxia of the fetus (the most dangerous situation for the crumbs);
- loss of the umbilical cord or body parts of the child in the birth canal, for example, with intensive discharge of amniotic fluid, with polyhydramnios;
- rupture of the uterus along the old scar during childbirth;
- high blood pressure in the parturient woman, eclampsia.
In case of premature commencement of labor, a woman who was scheduled to undergo a cesarean section for medical reasons in a planned manner, also has an emergency operation.
Important aspects
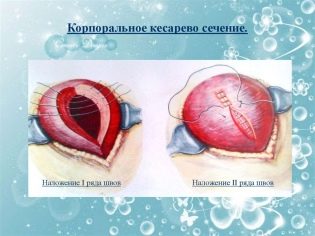
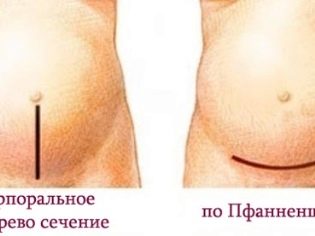
If for a planned operation it is considered preferable to have a horizontal incision just above the pubis, then for emergency surgery, surgeons often do not have time for such an incision. Therefore, such a delivery can be carried out by the corporal method. The abdominal wall dissection is carried out longitudinally, vertically from the navel perpendicular to the pubis line down.
The corporal incision provides a wider and faster access of the surgical team to the uterus. The uterus itself can also be dissected longitudinally, transversely, in a semilunar way - the choice of a particular tactic depends on the preferences of the surgeon performing the operation, as well as on the location of the fetus in the uterus and other factors.
The minus of tactics is that the risk of heavy and heavy bleeding during a corporal dissection increases significantly. But in situations where the countdown goes on for minutes and the life of a woman or a child depends on them, such a risk is justified, especially since modern maternity hospitals and perinatal centers have stocks of donor blood and plasma for immediate replacement of the amount of blood lost during bleeding.
Emergency caesarean section, if it passes without complications, lasts less than the planned, because the time for the abdominal wall dissection is less corporative way. Sometimes doctors, after weighing the risks, perform an emergency operation with a low horizontal section, which is more preferable if the woman is still going to have children.
Vertical seams on the abdomen heal longer than horizontal ones, they are not cosmetic, and therefore almost always spoil the appearance of the abdomen. Healing of sutures lasts about 60 days. For comparison, the suture after a planned operation heals three times faster - about 20 days.
Often, after an emergency operation, a woman and a child need to be in reanimation.
Anesthesia for urgent surgery
The choice of the type of anesthesia is another interesting feature of emergency surgical delivery. If an anesthesiologist examines a woman before a planned operation to select the type of anesthesia for the upcoming operation, there is simply no time to identify contraindications before an emergency operation. Today's epidural anesthesia has a fairly large list of contraindications, but general anesthesia, which until recently was the only type and had no alternatives, has no contraindications - it can be given to anyone at any age and in any situation.
The only thing that will matter is the history indicated in the woman’s card, its weight and the state of blood pressure at the current time. Based on these data, the anaesthesiologist will quickly determine the necessary dosages of drugs that will immerse the woman in strong medical sleep, in which she will neither see nor hear anything. Of course, she will not be able to see her baby immediately after birth.
Epidural anesthesia requires not only preliminary preparation, but also a longer time to achieve the effect. From the moment of introduction of drugs into the epidural space of the spine, it takes from 15 to 25 minutes before the onset of the necessary pain relief, while general anesthesia acts within a minute after the injection of an intravenous injection. It takes another five minutes for the doctor to install the tracheal tube and connect the patient to the ventilator. After this operation can begin.
If a woman has an epidural anesthesia at the beginning of labor and a catheter is already in her spinal canal, there may be spinal anesthesia, in this case, pain medication will be inserted into the installed catheter. A woman will be conscious, but she will not feel pain, she will be able to see the moment of birth of her child.
Possible consequences
Any cesarean always has a chance of becoming complicated. But with an emergency operation, the risk of negative consequences is much higher. What could be the consequences:
- adhesions, suppuration of the suture, formation of fistulas in the postoperative suture area on the abdomen, discrepancy of scars;
- infectious complications, inflammation;
- the likelihood of bleeding during the operation or after it in the early recovery period;
- inadequate reaction of the woman to anesthesia;
- the impossibility of repeated delivery through the natural birth canal;
- development of respiratory failure, distress syndrome in a child;
- effect on the baby drugs for anesthesia.
The recovery period after an emergency operation lasts almost a month longer than the same period after a planned operation.
The woman is being severely restrained on physical exertion, on weight lifting, and she is recommended a strict diet in order to prevent bloating and constipation.
It is possible that after a corpus dissection, the puerperal patient will have to take painkillers longer. In almost all cases after the COP, an emergency course of antibiotic therapy is conducted to reduce the likelihood of infection. This factor sometimes leaves an imprint on the breastfeeding regime - it is possible that it will be necessary to express and dispose of the milk before the end of taking antibiotics.
Learn more about caesarean section in the following video.