Frequent problems after cesarean section
A caesarean section is always closely related to possible complications. Compared with physiological labor, the risk of complications after surgical delivery is increased 10–12 times. At the same time, complications can develop at any stage - during the operation, immediately after it, some time after it and even months later. In this material, we will talk about what complications can be, how often they occur and what problems a woman may face after surgery.
Types of complications
Complications are early and late. It is customary to refer to all the problems that have arisen during the surgical intervention, as well as in the early postoperative period. Later are considered complications that emerged only after some time.
Problems can be contagious. The probability of infection when opening the abdominal cavity is very high. Even conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that inhabit the environment, on human skin, can become dangerous killers if they get into a more favorable breeding environment - inside the human body. Infectious complications are among the most dangerous, they are usually among the early complications.
Immunological problems are not excluded. The operation itself causes a decrease in the immunity of the woman, which can cause exacerbation of her chronic diseases (cystitis, pyelonephritis, diseases of the lungs, liver). In addition, sometimes immunity, the task of which is to protect the body from everything foreign and potentially dangerous, perceives suture as foreign material, which is used to sew incisions in the uterus and skin of the anterior abdominal wall. And then rejection of the filaments is not excluded, which leads to problems with the healing of the seams.
Physiological problems are not excluded - the dissected uterus refuses to contract normally, and then it is impossible to do without medical assistance. Atony and hypotension of the reproductive female organ are dangerous conditions.
Complications are traumatic. They occur through the negligence of a physician, who may injure vessels, large blood nodes during the operation, as well as the uterus, bladder, intestines, and ureters. In this case, rapid response measures are needed to correct the situation as soon as possible. The woman herself can be injured if she does not follow the medical recommendations regarding the limitation of the mode of physical activity after the operation.
All complications are divided into three large groups:
- internal;
- on the seams;
- after anesthesia.
The likelihood of complications depends on many factors:
- lifestyle (women who smoke, use alcohol and drugs are more susceptible to negative consequences);
- age (the parturient age to 19 years and after 36 years are most dangerous);
- gynecological history (the number of births, abortions, inflammatory processes, tumors of the reproductive organs);
- the presence of chronic diseases;
- obesity, preeclampsia;
- from the selected technique of the operation and the quality of the used suture material
On the most common problems of the postoperative period will tell more.
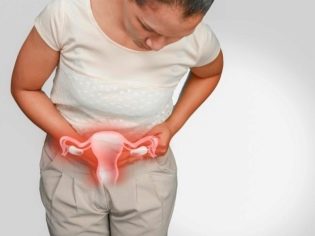
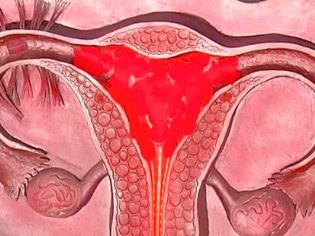
Endometritis
Inflammation of the internal functional layer of the uterus during physiological labor occurs only in 1-2% of cases, and after operative delivery the incidence of inflammatory complications occurs in 15-20% of cases. The illness can appear the next day after the operation, and it can only be felt in a few weeks. Most often, the disease manifests 3–6 days after surgery.
At the same time, there are pains in the lower abdomen, back and lower back pain. The temperature rises and stays at high elevations for a long time. Inadequate stages of rehabilitation can be observed from the genital organs. The woman feels a breakdown, a fever.
If you detect such signs, you must immediately inform your doctor and start receiving treatment. Antibiotics are commonly used for therapy.
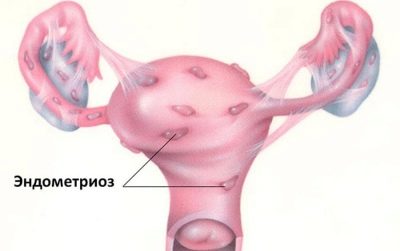
Endometriosis
This disease most often refers to late complications and problems that are significantly delayed in time. The disease develops when the epithelium cells spread to other tissues for which the epithelial layer is not natural. During surgery, the transfer of endometrial cells is purely mechanically very likely. They may be in other tissues and organs.
Cells do not die and continue to live. They depend on hormones, and therefore every menstrual cycle in them will occur the same processes as in endometrial cells located in its place. Sometimes problems are detected only a couple of years after cesarean, and sometimes endometriosis is diagnosed after the woman’s treatment for secondary infertility.
Symptoms are very individual. There may be pelvic pain. For some, they are aggravated before menstruation, and for some it seems that the “womb hurts” almost constantly. There may be unpleasant painful feelings during intercourse, during bowel movements. Over time, the development of infertility is likely.
Treatment may be conservative (hormonal drugs), but laparoscopic removal of the affected areas with subsequent hormone therapy is considered more effective.
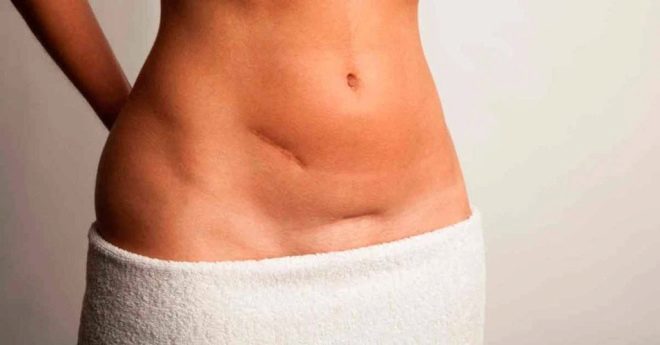
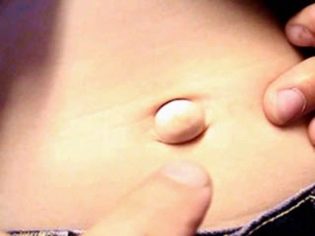
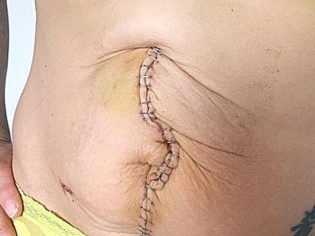
Navel hernia
This complication occurs in those who during the operation did a vertical incision. The umbilical hernia is considered a late complication and, at best, is found after a few months, at worst - the hernia sac becomes apparent only during the carrying of the next child.
The reason for the formation of a hernia may be poor-quality suture material, immune rejection of part of the suture material in the early postoperative period, as well as infection of the suture, which greatly slowed its normal healing. Sometimes the cause of a hernia is a trivial error of a surgeon who inaccurately joined the abdominal muscles dissected during the operation. Lifting weights and irrational exercise after a cesarean section also cause a hernia.
Conservative treatment of such a hernia is not appropriate, according to medical standards surgical treatment is preferable.
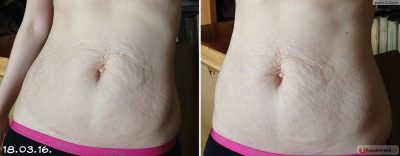
Weakness or atrophic changes in the abdominal muscles
The stomach after surgery in the early period, all looks a bit saggy, but the true problems are found later. The weakness of muscle tissue can gradually lead to atrophic changes in which part of the muscle tissue is replaced by connective. A woman can not get rid of the hanging "frog" belly, it hurts her to do physical exercises on the press, it is difficult to get up from a prone position.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, acupuncture help restore the muscles of the former tone, restore the broken nerve connections in the muscle tissue. In the absence of the effect of conservative treatment, plastic surgery is prescribed.
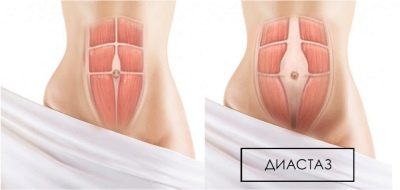
Diastasis
This problem is very widespread.After cesarean divergence of the abdominal muscles, pathological relaxation of the midline of the abdomen is diagnosed in four women out of ten. The median line is restored after physiological labor faster than after cesarean, in which the abdominal wall is inevitably injured by a scalpel.
Relief of diastasis can be facilitated by special therapeutic exercises, a proper balanced diet, but in the absence of the desired effect, surgical repair of the abdominal muscles is recommended for the woman.
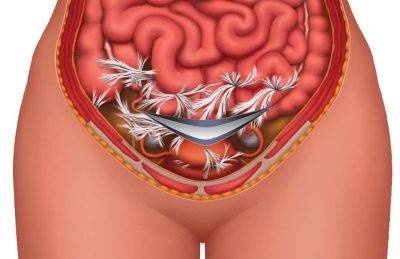
Spikes
Adhesions after surgery may form as a defense mechanism - this is how the body tries to close the pathways for the infection to spread. As a result, some internal organs are sticking together - loops of the intestine, uterus, appendages. Adhesions may occur anywhere in the abdominal cavity.
Can manifest painful sensations and dysfunction of organs affected by adhesions. Painful sensations can be in the stomach, intestines, with the defeat of the reproductive organs, the right or left side (ovary) hurts.
Spikes are always easier to prevent than to cure. Therefore, they ask women to get out of bed as soon as possible after surgical childbirth, to move as much as possible, but carefully and delicately. If the adhesions did appear, their laparoscopic removal is considered effective.
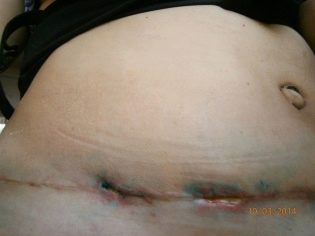
Problems with stitches
The early problems of postoperative suture include increased bleeding, hematoma formation, purulent and inflammatory processes, immune rejection of suture material. Normally, the healing of external seams takes up to 20 days, if the seam is horizontal, and up to 60 days, if it is vertical.
Late problems with sutures are the formation of hernias due to the presence of early complications and violations of the requirements for the rehabilitation period, fistulas, pathological growth of connective tissue and the formation of keloid scar.
Many problems can be avoided by properly treating the seam, observing the ban on lifting weights and making sharp movements. Pain in the seam, redness, discharge from it (blood and purulent, blood) should immediately alert the woman and cause her unplanned treatment to the doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable here.
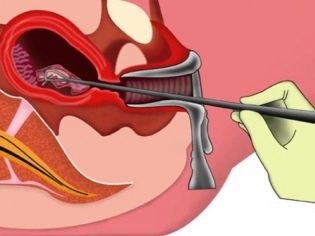
Hematometer
This term refers to the violation of the outflow of lochia after surgery from the uterus. The main symptom is a sudden cessation of discharge. Normally, they last up to 6–8 weeks after delivery. If after 7 days the discharge suddenly ended, there was a feeling of fullness in the uterus, periodic spastic pain, then analgesic candles and "No-shpa»Do not help, the hematometer itself will not pass. An urgent need to consult a doctor.
A woman will be probed the uterus, if necessary, vacuum aspiration or cleaning of the uterus to release it from the accumulated contents.
Exacerbation of chronic diseases and acute diseases
Since the surgical procedure severely undermines the state of immunity, the exacerbation of chronic illnesses may well manifest itself within a few days after surgical delivery. Pain when urinating, feeling that the entire bladder hurts may indicate that cystitis is quite common in women.
If you have a headache, the temperature has risen, a cough has appeared, it is possible that weak immunity could not become a barrier for viruses and the most common SARS started for the woman.
Complications of anesthesia
Modern drugs that are used for anesthesia, rarely cause complications, but this is not completely excluded. According to reviews, general anesthesia is the hardest of all. After it stirs up, nauseated, the woman comes out of this state quite hard.
After the now popular epidural anesthesia, in which the drug is injected into the spine, severe headaches are often observed, which can persist for several days and several months. And also there is a backache.
On the child's body, both types of anesthesia have an effect. The baby is born somewhat inhibited, it takes the breast worse. But this is a temporary phenomenon. Lactation after surgery also comes late for a few days.
On the pros and cons of cesarean section, see the following video.