Acetonemic syndrome in children
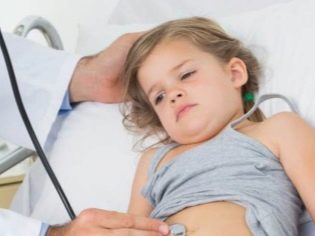
The smell of acetone from the baby’s mouth and occasional vomiting is a reason for going to the doctor. It is possible that the case in acetonemic syndrome, which requires a mandatory individual approach.
What it is?
Acetonemic syndrome in children is not considered a separate disease, it is a complex of symptoms associated with the accumulation of ketone bodies in the blood plasma of a child. In medicine, the syndrome has other names, for example, non-diabetic ketoacidosis or acetonemic vomiting.
The specified pathological condition occurs mainly in children therefore, it is considered a typical childhood pathological condition. Sometimes there is no rational explanation for such attacks of vomiting, the syndrome is considered idiopathic or primary. This occurs in about 5% of children under the age of 12 years. In this case, girls are more prone to violation than boys.
If the basis of the symptom complex is a specific disease, the syndrome is called secondary. As far as it is common, doctors around the world find it difficult to answer - such statistics simply do not exist.
Ketone bodies that accumulate in blood plasma in children are acetone, b-hydroxybutyric acid, acetoacetic acid. If the syndrome is an independent idiopathic symptom complex, then usually acetonemic crises develop with large periods of time between meals (on an empty stomach).
Secondary acetonemic syndrome develops on the background of uncompensated diabetes mellitus, with thyroid gland diseases, craniocerebral injuries, the presence of brain tumors, after serious poisoningif there was a toxic effect on the liver, with severe infectious intoxication, leukemia.
The reasons
Speaking of acetonemic vomiting syndrome, it should be understood that it’s still about idiopathic acetonemia and not secondary. If the accumulation of ketone bodies is associated with the main disease, then the description of the syndrome as a separate complex of symptoms does not make sense - the disease is detected and treated as a specific disease should be treated. We will talk about the state when the baby is generally healthy, but sometimes parents notice the smell of acetone from his mouth, as well as bouts of vomiting, which can not be explained.
Ketone bodies can accumulate in the blood plasma of a baby who receives little carbohydrate with nutrition. Also, the primary cause can be excessive fat intake. In the liver of children, less enzymes are produced that are involved in the metabolic processes of oxidation. Also, due to natural age factors, all children have lowered the intensity of the splitting process and the output of ketone bodies.
There are several theories of the origin of child acetonemic syndrome. According to one version, vomiting begins as a result of the fact that the concentration of glucose in a child’s blood decreases, if he is hungry and the body begins to create backup energy sources - these are ketone bodies. But their large number causes intoxication and irritation of the digestive tract organs. From here and emetic manifestations.
According to another version, the concentration of glucose in the body of a child can decrease faster than the level of ketone bodies, and therefore this imbalance occurs.
But all researchers agree that starvation or an infectious disease in the acute phase is usually the starting mechanism.An accumulation of stress, psychological instability, a long stay in the open sunlight, hunger and overeating, too much eating protein and fat in the absence of an adequate amount of carbohydrate foods can cause an acetonemic vomiting.
In newborns, such vomiting is usually associated with the fact that their mothers in the late periods suffered from preeclampsia in edematous form and nephropathy.
Symptoms and signs
To a greater extent, according to the observations of pediatricians, children with highly excitability in the organization of the nervous system are susceptible to such a syndrome; A manifestation of the syndrome is acetonemic crisis - a pathological condition that has arisen spontaneously and suddenly or after the appearance of “precursors” (some children experience weakness before vomiting, refuse food, complain of headaches).
The crisis itself is repeated severe vomiting, which develops in response to any attempts to feed or water the child.
Moreover, it is not even the vomiting itself that is dangerous, but the fact that the signs of intoxication and dehydration are growing very intensively. - the toddler becomes inelastic skin, dry mucous membranes, he cries without tears, the skin visually turns pale. With a severe crisis, the development of a convulsive syndrome is possible.
Body temperature rises to 37.5-38.5 degrees. The child complains of abdominal pain, maybe constipation or loose stools as a concomitant disorder. Most often, the very first symptoms of having acetonemic syndrome manifest by 2-3 years, may worsen by the age of 6-7 years and completely disappear by the time the child reaches the age of 12 years.
From any other vomiting, acetonemia is distinguished by the characteristic odor from the baby’s mouth - some compare it with rotten apples, some - with fume. This acetone odor may appear even at the “forerunner” stage, that is, before the onset of vomiting. It smells not only from the mouth, but also from urine. Sometimes the smell is caught only in the immediate vicinity of the baby, and sometimes even at a distance of several meters.
What to do?
It will be erroneous to resort to popular and non-traditional means. It is better to start with a visit to a pediatrician, who will find out exactly whether the pathology is primary or secondary. The child will be prescribed laboratory tests. With the specified pathological condition, blood tests are usually characterized by leukocytosis, elevated neutrophil count, and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Ketone bodies are found in the urine.
It is very important to visit a doctor with a baby, because these symptoms are quite similar to appendicitis, peritonitis, meningitis, encephalitis, brain tumors, poisoning and even an intestinal infection. Only a qualified medical professional can distinguish one from the other.
Treatment
To treat acetonemic syndrome should be a complex, and the main task is the correct way out of crises and the prevention of repeated attacks. If the child is small, then dehydration can be deadly for him. Therefore, babies should be hospitalized in a children's hospital, where medical workers will not allow dehydration. Diet for acetonemic syndrome requires a rather rigid restriction in the diet of fats, but it is recommended to consume carbohydrates that are quickly absorbed without any load (from cereals, cereals). The menu should be provided with a special drinking mode - you need to drink often and little by little.
Some of the ketone bodies that have entered the intestine can be neutralized by means of sodium enema (a solution of sodium bicarbonate is used for its preparation). With acetonemic vomiting, the child is recommended for oral rehydration (replenishment of water-salt balance). To do this, use "Regidron", "Humana Electrolyte", and also alkaline mineral water or house salt solution according to the method of Dr. Komarovsky.
The child may be given antiemetic drugs, for example "TSerukal", antispasmodics, herbal sedatives. With the right approach, aimed at eliminating dehydration, the symptoms of a crisis go to naught for 2-4 days.
Between attacks, parents should not allow periods of prolonged starvation.
The child should be regularly shown to the district pediatrician. Carefully need to follow the diet, it should not be an abundance of fatty foods, preference should be given to dairy products, vegetables and fruits. Particular attention should be paid to the prevention of seasonal and catarrhal diseases. It is important not to overload the psyche of the child, to monitor his emotional and psychological well-being. Hardening and swimming are helpful. It is important to ensure that the child gets enough sleep.
Sometimes doctors consider it necessary to prescribe for the course of treatment course intake of vitamins, enzyme preparations, massage. Pharmacies are available rapid tests for the determination of acetone and ketone bodies, with their help, parents can independently monitor the condition of the child, conducting a urine test at home.
When acetonemic syndrome is detected and confirmed in a baby, it must be registered with a children's endocrinologist. A child will be removed from the register if there have been no repeated crises for 3 years, and the annual surveys did not show any deviations in the analyzes.
More on the syndrome says Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.