What should be the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy?
Expectant mothers are always very interested in how much weight their baby will be born with. Therefore, they are keenly interested in how much the crumb weighs while still in the womb. This question is important for doctors. Although the weight of the fetus is called the estimated, but even it allows you to learn a lot about the development of the baby. What is usually the weight of the crumbs in the womb during different periods of pregnancy and what it depends on, we will tell in this material.
How does a baby grow?
At the very beginning of pregnancy, all the crumbs, regardless of gender, race, heredity, grow quite the same, adding millimeters and grams to their tiny weight weekly. All embryos grow at about the same speed, and only then, when the individual characteristics of the little man begin to appear, do the differences begin to appear.
It is possible to measure the growth of the fetus even the most modern ultrasound machine only in the second half of the first trimester. Up to 8 weeks, only the diameter of the ovum is measured, and this criterion is considered the main one, indicating the growth of the embryo.
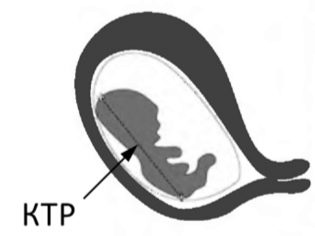
The size of the crumbs themselves is not yet available for measurement, the only exception is the coccyx-parietal size, but it does not give grounds for calculating the weight of the embryo.
Talking about the mass of the fetus for the first time is possible with the passage of ultrasound, starting at 11 weeks. It was at this time that the first differences between babies begin to appear - some babies more, others less. At 7-8 weeks the baby weighs about 3 grams, but it is so small that the weight does not have diagnostic value.
After 12 weeks, the baby begins to actively gain weight, sometimes doubling its mass in just one week. At this time, all organs and systems, as a rule, are formed; a period of their intensive growth and improvement begins. Gradually, the crumb begins to stock up on subcutaneous fat, hence the rapid weight gain. The biggest increase awaits the crumb in the third trimester.
In recent months, the child is already ready to be born physiologically, it remains only a little "get better", all organs and systems work. Since a fairly grown up baby can no longer actively move in the uterus, sleep and occasional unsharp movements in the close uterus become its main occupation. Over the past two months, the baby is gaining the weight that he will have at birth, and only in the last days before giving birth the weight gain almost stops.
From the end of the second trimester, female fruits are gaining slightly less than kids boys. Therefore, in the third trimester, they almost always differ in more miniature forms, although this is not a one hundred percent rule - there are girls who, by weight, can leave behind any little boy.
What affects the mass?
The weight of the fetus primarily affects heredity. If mom and dad are big and big, then the probability that they will have the same “hero” is more than 90%. Miniature, low, thin mom and dad usually give birth to a baby with low weight. To influence this pattern to any factors from the outside is quite difficult.
However, pregnant women should remember that there are factors that can not affect the body weight of the baby. First of all, it is food. If a mother eats well, balancedly, then her baby along with the blood will receive a balanced set of useful substances that will help him develop and grow harmoniously. If the future mother overeats, enjoys carbohydrates, cakes, baking, abuses vitamin complexes, even if she does not have a deficiency of vitamins, then the child receives all this through the uteroplacental bloodstream. The weight of the mother is growing, the weight of the baby is also growing.
If the mother’s nutrition is insufficient, scarce in vitamins and minerals, proteins and carbohydrates, then the child, willy-nilly, suffers a shortage of much-needed substances, his body weight will be less than it could be with regard to genetic features.
Smoking during pregnancy can also affect fetal weight. In 70% of pregnant smokers are born children with underweight. In the same way, alcohol, and narcotic substances, and even the usual medicines that mother took during pregnancy affect the fetus. Adversely on the body weight of the baby affect the mother's nervous stress and feelings, hard physical work, working conditions in hazardous production.
Some chronic diseases that the expectant mother has also affect the weight of the baby. For example, in case of diabetes or gestational diabetes, first manifested already in the period of gestation, there is a chance to give birth to a large or even a giant baby, whose weight will exceed 5 kilograms. A lack of mass of the fetus can manifest itself in chronic diseases of the kidneys, liver and heart in a woman.
Features of the course of pregnancy can not affect the weight of the child. If everything runs smoothly, then there is nothing to worry about. But the baby, which develops in conditions close to extreme - against the background of the threat of miscarriage, with other complications of gestation, is unlikely to be a hero.
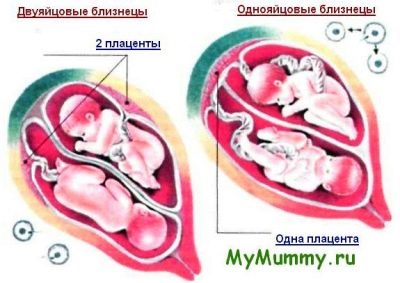
If the pregnancy is multiple, the woman bears two or three babies, then the weight of each will be less than the norm, and this is quite natural.
How is it determined?
Obstetricians and gynecologists use several formulas to calculate the expected weight of the fetus. If you want to try to calculate how much the baby weighs, the mother can independently.
Formula Lankowitz
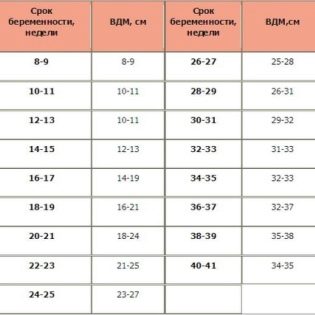
Experts consider this method of calculation to be the most accurate, although unfortunately it does not go without errors. For calculations, a woman will need to look at her exchange card at the page of the last visit to the doctor. There she will find two important parameters for the calculation - her abdominal circumference (OJ) and the height of the uterus floor (VSDM or VDM).
Both of these values add up, after which the resulting amount adds the mass of the mother in kilograms and her height in centimeters. The resulting number is multiplied by 10. For example: the gestation period is 30 weeks, the abdominal circumference is 110, the height of the uterus bottom is 30. The height of the pregnant woman is 170 cm, the weight is 70 kilograms. (30 + 110 + 170 + 70) х10 = 3800. The error in this calculation can be up to 0.5 kg. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that a woman has a big baby - his real weight in this period already exceeds 3 kilograms.
Formula Bublychenko
For calculation, you need to know only the body weight of the future mother at the current moment. Her weight is divided by 200, the resulting number is multiplied by 10. For example, the weight of a woman is 80 kilograms. (80/200) x10 = 4. The error with this method is large, it fluctuates within a kilogram, which is why obstetricians have recently tried to avoid using this formula
Formula Yakubova
For these calculations, a woman who has decided to practice arithmetic and satisfy her maternal curiosity will need data on the height of the bottom of the uterus and the circumference of her belly. You can find them in the exchange card, these data are entered into it at each scheduled admission. WDM is added to the abdominal circumference, and the resulting amount is divided by 4 and multiplied by 100. For example, WYD - 30, abdominal circumference 100. (30 + 100) / 4 = 32.5.When multiplied by 100 it turns out 3250 gr.
Formula Jordania
To calculate again, you will need to know the height of the bottom of the uterus and the circumference of the future mother's belly. These values multiply each other. For example, WYD -30, circumference - 100, it turns out that the estimated weight of the child is 3 kilograms.
Ultrasound
The most accurate are the calculations that are done by sonographic method, that is, by ultrasound. To derive the putative body mass of a child, special equations are used, which are compiled by the scanning apparatus software, the Headlock method is most often used.
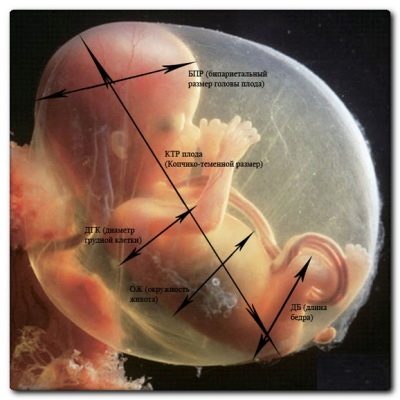
The required mathematical values for the equations are the dimensions that the somnologist determines on ultrasound. it bipariental size of baby's head, length of the femur, tummy circumference and head.
To make it clearer, we present these equations using the two most popular calculation methods (according to Headlock and Shepard):
- Shepard - Log10 BW = -1.7492 + 0.166 (biparient size) + 0.046 (fetal tummy circumference) - (2.646 [(tummy circumference) X (biparietal size)] / 100).
- According to Headlock - Log10 BW = 1.3598 + 0.051 (Circumference of a child’s abdomen) + 0.1844 (length of the femur) - 0.0037 (abdominal circumference X length of the femur), or Log10 BW = 1.4787 + 0.001837 (bipartial size heads) 2 + 0.0458 (abdominal circumference) + 0.158 (femur length) - 0.003343 (multiply abdominal circumference by the length of the femur).
Thus, the measured parameters of the baby become components of the mathematical expression, as a result of which the computer produces the result. It is usually indicated in the protocol of ultrasound diagnostics in the section “Estimated Fetal Weight”. The error in singleton pregnancy is from 8 to 10%, when carrying twins, the error increases to 15%.
This method can not be called exact, as in a pharmacy, but medicine has not yet invented anything more precise.
It is on the basis of the ultrasound data that all the currently existing fetal weight standards for weeks and months of pregnancy have been created.
Norms in different terms
What should be the body weight of a child who has not yet come into the world is definitely hard to say, because we are all different - high, low, thin and full. Babies in the womb also have individual traits. Therefore, there may be variation, but mean values do exist.
Starting from the 11th week of pregnancy, ultrasound machines can already calculate the first weights:
Obstetric term, week | Estimated Weight (grams) | Obstetric term, week | Estimated Weight (grams) |
11 | 11 -14 | 26 | 969 – 1000 |
12 | 19 – 25 | 27 | 1135 – 1200 |
13 | 31 – 40 | 28 | 1319 – 1400 |
14 | 52 – 65 | 29 | 1482 – 1530 |
15 | 77 – 105 | 30 | 1636 – 1690 |
16 | 118 – 135 | 31 | 1779 – 1830 |
17 | 160 -180 | 32 | 1930 – 1990 |
18 | 217 – 230 | 33 | 2088 – 2180 |
19 | 270 – 300 | 34 | 2248 – 2300 |
20 | 345 – 375 | 35 | 2414 -2500 |
21 | 416 – 460 | 36 | 2612 – 2690 |
22 | 506 – 130 | 37 | 2820 – 2910 |
23 | 607 – 640 | 38 | 2992 – 3000 |
24 | 733 – 800 | 39 | 3170 – 3250 |
25 | 844 – 900 | 40 | 3373 – 3500 |
This table is compiled without regard to the sex of the child. Some experts who want to achieve the greatest accuracy in situations where the mode of delivery depends on the expected weight and other important issues, use the tables developed by doctors from Germany to measure the weight of children of European appearance in the early 90s of the last century. It is based on the sex of the fetus.
Table of normal values of the estimated weight of babies of different sexes:
Obstetric term, weeks | Estimated weight of the male fetus, allowable fluctuations (grams) | Estimated weight of the female fetus, allowable fluctuations (grams) |
23 | 600 (420-770) | 580 (400-750) |
24 | 690 (480 -880) | 670 (460 – 860) |
25 | 800 (540 -1030) | 760 (520 -990) |
26 | 940 (610 -1180) | 880 (590 -1140) |
27 | 1080 (690 – 1360) | 1000 (650 – 1300) |
28 | 1220 (750- 1520) | 1120 (710 – 1460) |
29 | 1350 (830 – 1710) | 1250 (790 -1650) |
30 | 1520 (940 – 1910) | 1420 (900 – 1850) |
31 | 1690 (1070 – 2110) | 1590 (1010 – 2050) |
32 | 1890 (1200 – 2360) | 1790 (1140 -2280) |
33 | 2130 (1360 – 2690) | 2030 (1300 -2610) |
34 | 2390 (1600 – 3000) | 2270 (1530 -2920) |
35 | 2640 (1870 – 3320) | 2550 (1790 – 3230) |
36 | 2860 (2140 -3550) | 2760 (2060 – 2460) |
37 | 3090 (2400 – 3770) | 2970 (2290 – 3650) |
38 | 3300 (2620 – 4000) | 3160 (2500 – 3850) |
39 | 3470 (2760 – 4180) | 3320 (2670 – 4020) |
40 | 3600 (2910 -4350) | 3450 (2800 – 4180) |
German tables, which are used throughout the world, begin at 23 weeks of pregnancy is not accidental. It is at this time in children of different sexes that the body begins to form according to sex characteristics, which is why weight gain in boys and girls begins to differ from each other. In earlier periods, this difference between heterosexual babies is not present or it is not pronounced enough and remains unnoticed for diagnosis.
Deviations from normal values
It is considered normal if a child is born on a period of 39-40 weeks with a weight of 3000 to 3800 g. However, those babies who are born with a weight of up to 3 kilograms and those who have more than 4.5 kg of weight at birth have neonatologists fear not cause.
Obstetricians urge future mothers not to panic about the difference in the numbers presented in the reference tables and their real numbers.
First, you should always make an error correction (plus or minus 500 g at a minimum), and secondly, the kids grow “jumps”, so at 34 weeks a crumb can upset mom by lagging behind the average standards, and by 36 weeks to reach normal average or even close to the upper limit of normal.
If the baby during all ultrasound studies during pregnancy demonstrates stubborn excess of the norms, they talk about a large fetus. The trend towards a large baby can be seen in the second trimester. Based on a single ultrasound such conclusion cannot be made several studies are required within a few weeks.
At the same time, attention is also paid to instrumental measurements - the abdominal circumference of the future mother and the height of the uterus. When a large fetus is usually, WDM exceeds the norm (at 32 weeks at a rate of 32 cm, for example, this parameter is increased to 34 cm, and at 36 weeks instead of the set 36 cm it is about 39 centimeters).
If the baby in the womb noticeably lags behind the mean values and during several diagnostic measurements it “passes” only at the lowest limit of the norm (5th percentile), then the doctors prescribe an additional examination, the purpose of which is to reveal the viability of the uteroplacental blood flow, possible fetal pathologies, including hereditary and chromosomal, intrauterine growth retardation, the presence or absence of intrauterine infections, rhesus conflict.
To do this, carry out ultrasound expert class, USDG, make tests for infections, clinical blood and urine tests. If necessary, a woman is sent for a consultation to genetics and the passage of invasive diagnosis in order to identify chromosomal abnormalities.
It is up to the expectant mother to agree to such measures, especially since modern medicine is ready to provide a harmless but expensive alternative to invasive diagnostic methods - a prenatal DNA test for blood analysis from a mother's vein.
A woman with suspected fetal hypotrophy is given regular monitoring of the condition of the baby using cardiography (CTG), and additional treatment is prescribed (sometimes in the hospital), which includes taking vitamins and drugs to improve uteroplacental blood flow. The estimated weight of the crumbs is controlled by intermediate ultrasound examinations.
Lagging behind the norms is not considered particularly dangerous if all the parameters of the baby are reduced symmetrically.. Then this may be a variant of the norm, an anatomical feature of the child.
Beginning with 7 months of pregnancy, the weight of the baby is not only the subject of burning curiosity of expectant mothers, but also important information for obstetricians. On the basis of general data on pregnancy and the approximate weight of the crumbs, they draw conclusions about how best to give birth to a child.
For large fetuses, cesarean section is often recommended; if the size of the fetus does not match the size of the pelvis, even if the baby’s mass itself is normal, it is also recommended to perform a caesarean section.
The accuracy of the determination and error
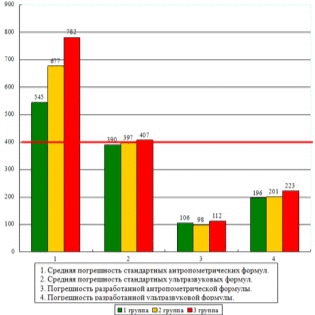
As mentioned above, the most accurate is the method of determining the estimated weight of the baby in the womb by ultrasound. According to data obtained by American doctors from Florida, the error in calculating the Headlock was approximately 14% of the baby’s body weight. In other words, the real mass differed from that predicted by the apparatus by 14% in one direction or another. Today it is the highest result.
The methods used by midwives before the widespread use of ultrasound, formulas and measurements, are practically not used today, because there is no need for them. For information about the possible body mass of the crumbs do not need to count anything. Calculate everything will help a computer program.The accuracy of the formulas (presented above and some others) is estimated at about 40-55%. While on ultrasound, the accuracy of estimating a child’s body mass gains almost 82%.
The most accurate method, as gynecologists like to say, is weighing. Therefore, those who want to know how much grams the child weighs, you just need to be patient and wait for the birth. They will answer this question with exhaustive accuracy. All other methods resemble fortune telling. The size of the bones and the head of the baby, even on ultrasound, can talk about weight only indirectly, because there are children with long legs (to the mother), but thin or large head (to the father).
Doctors themselves argue that the accuracy of determining the weight of the fetus can affect the quality of imaging during the ultrasound. If a woman is full, has extra pounds, fat deposits on the abdomen, then the error will increase. If a woman’s pregnancy occurs on the background of low water, the probability of a more significant error than 14% of body weight also increases. It is more difficult to calculate the weight of babies during pregnancy twins, especially on long terms, because the limbs of one baby on ultrasound is easy to take on the limbs of another, as a result of which a significant error can creep into the predictions of body weight of babies.
If a child has developmental pathologies (hydrocephalus, microcephaly, gastroschisis), it is difficult to determine its expected weight, because the dimensions important for the preparation of mathematical equations will not reflect the actual weight of the child.
Reviews
Feedback from women in the forums devoted to issues of pregnancy and motherhood is dominated by reviews about the erroneous determination of the weight of the child before delivery. Most young mothers emphasize that the weight predicted less than it actually is, with the difference ranging from 100 grams to a kilogram.
Women who, by coincidence, did two ultrasound examinations on the same day in two different places on two different devices, arguing that the calculations of the estimated body weight of the baby were markedly different from each other. The “hit” closest to the truth was if a three-dimensional ultrasound was done.
All about the weight of the fetus for weeks, see the following video.