Why determine FCMK during pregnancy and what to do with an increased rate?
Blood clotting rates are very important. Their importance increases significantly during pregnancy. One of these indicators is RFMK.
What it is?
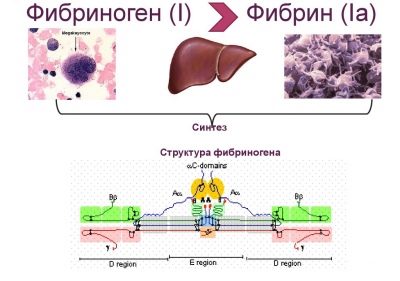
RFMK is an incomplete name for a laboratory marker. Doctors call it soluble fibrin monomer complex, but in practice, the abbreviation RFMK is much easier to use.
By its chemical structure, this substance is a special form, where fibrinogen binds to its precursors by homeostasis. PKMK molecules are actively distributed throughout the bloodstream. You can determine them with the help of special tests for the determination of hemostasis indicators.
Fibrinogen and its metabolic products are very important for the body. The final stage of the homeostasis reaction is the formation of a blood clot. Such a reaction is necessary and physiological.
If blood fibrin clots in the human body were not formed, then he could have died from any, even minor bleeding.
The formation of a fibrin clot is gradual. First, two of its monomers - A and B - are split off from the native fibrinogen molecule - thrombin contributes to the development of this reaction. The next stage is the addition of ionized calcium molecules to these monomers. It is at this stage that the blood clot begins to physically build up.
The change to a more dense texture occurs under the influence of a special enzyme - fibrin ligase. It is also called the XIII coagulation factor. Such a complex cascade of biological reactions is necessary for the body to be physiologically protected from any blood loss or bleeding.
Doctors consider PKMK to be an important clinical sign of the course of the process of intravascular coagulation. Evaluation of this indicator allows specialists to identify violations that occur at the earliest stage of their formation.
Norms
Experts have established the normal values of the substance in the blood. The average rate is from 3.3 to 4 mg / 100 ml.
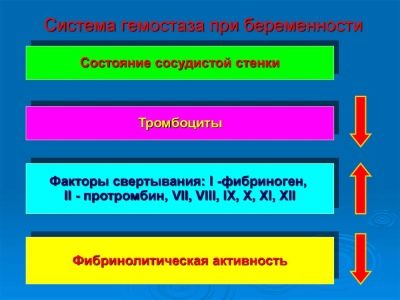
The values of this laboratory marker during pregnancy may vary. These changes are most pronounced by the 3rd trimester. In this case, most women have a fairly high level of PKMK in the blood.
The doctor will almost never appoint a future mom to take only one measure of hemostasis. Typically, the definition of pathology requires the definition of many combined clinical markers.
This leads to the fact that the future mommy should also donate blood for the determination of D-dimer, APTT and other indicators of hemostasis.
The researchers found that the first changes in coagulability of blood in pregnant women begin to occur by 13-15 days from the moment of conception, that is, after fixing (implantation) of the baby to the wall of the uterus. If this process is completed successfully, then this is evidence that the child’s active blood vessels become active.
Doctors also call this new blood flow system fruit. The active work of the baby’s blood vessels and provokes changes in his mother’s hemostasis. As the fetus grows and develops intrauterinely, RFMK blood counts in his mom will also change.This usually happens gradually and weekly.
The growing fetus contributes to the fact that in the maternal organism, a gradual increase in the concentration of the fibrin complex complex begins. A statistically significant increase in the rate occurs by the second trimester of pregnancy. In the first weeks after conception, the concentration of the complex complex complex does not change significantly.
In the future, the level of blood in the PFMC only continues to increase.
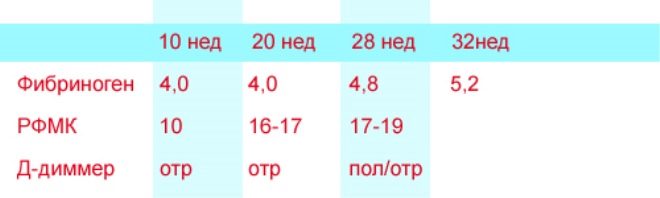
It is important to note that during different periods of gestation of pregnancy indicators of this indicator in the blood of pregnant women are different. Doctors use special tables. They indicate the normal values of the studied laboratory parameters. One of these tables is shown below:
Gestational age | Normal concentration of fibrin complex (mg / 100ml) |
1 term | 5,5 |
2 term | 6,6 |
3 term | 7,5 |
A careful analysis of the table allows you to see that this indicator is significantly increased by the final period of carrying a baby. The nature of this change is not accidentally invented. The body of the future mother thus preparing for the upcoming serious blood loss.
It is important to note that not only the concentration of PCMC changes, but also other clinical indicators of hemostasis.
Reasons for raising
Increased CPMC may not only be physiological. In such a situation, violations occur much faster than by the third trimester of pregnancy.
Many expectant mothers have such deviations may occur by 26-28 weeks, and even earlier. These violations already indicate the presence of trouble in the female body. In such a situation, the obligatory determination of the cause that led to the development of such changes is required.
Positive RFMK values in the blood are not the result of any pathology. Normally, this substance is always determined. Doctors evaluate not the presence, but the level of the FEMC in the blood.
If the concentration of this substance in the blood of the expectant mother is significantly increased, then additional diagnostics are required in order to identify the cause that led to the development of these changes.
With thrombosis, the level in the blood of the PMMC rises. Usually the risk of developing this pathology is significantly increased in pregnant women. The tendency to thrombosis is also present before pregnancy. On the development of this pathology affects heredity.
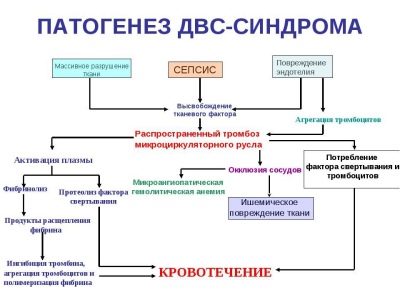
DIC syndrome (disseminated vascular coagulation syndrome) is accompanied by changes in blood flow and viscosity. One of the changing laboratory criteria is RFMK.
The more pronounced this pathology, the higher the blood concentration of this indicator.
In women suffering from severe toxemia or having preeclampsia, hemostasis is also impaired. In the high-risk zone are also future moms who have twins or triplets.
Women who have undergone in vitro fertilization should also be tested more often. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the level of the PCM and other hemostasis indicators more carefully. If the expectant mother is forced to take hormonal drugs during pregnancy, this can also lead to an increase in this indicator.
Women who continue to smoke or drink while carrying babies are also at increased risk of developing such disorders.
Doctors recommend monitoring RFMK in the blood and expectant mothers with various rheumatologic diseases and pathologies of the cardiovascular system. If a woman has an arrhythmia or an abnormal heart rhythm, then in this case, an increase in the amount of PKHM in the blood can be dangerous for her.
Even ordinary infectious diseases can lead to an increase in this substance in the blood. In this case, the concentration in the blood FPCM increases slightly. After normalization of the general condition, hemostasis indicators return to normal.
Diseases of the endocrine system can also cause an increase in fibrin monomer complex.Thyroid pathologies and diabetes mellitus are the most common diseases that trigger the development of such disorders.
How is a blood test performed?
The method of conducting this laboratory test is very simple. For this purpose, venous blood is collected. A future mother can undergo such research both in the clinic and in a private laboratory. To hand over this analysis is better according to the recommendation of the doctor. If the woman has any pathology of hemostasis, the therapist or hemostasiologist will send the future mother to the study.
Pass the study should be strictly on an empty stomach. To obtain more accurate results, you should limit the consumption of fatty and fried foods on the eve of the trip to the laboratory. Before donating blood, you can only drink some water.
Special training before going to the laboratory is not required. Doctors recommend only to eliminate the use of anticoagulants before the study. This should be done 1-2 days before going to the laboratory.
Before discontinuation of these drugs should always consult with your doctor.
Implications for the child
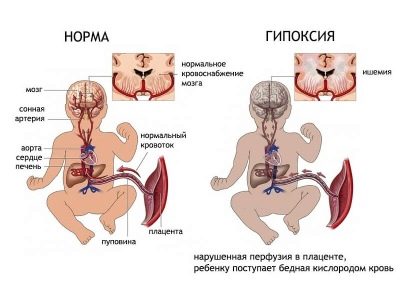
An increase in the amount of fibrin monomer complex in the blood leads to the fact that numerous blood clots appear in the system of the general blood flow between the mother and the fetus. They block the lumen of the arteries, which leads to a decrease in the supply of various nutrients to the baby. Such a situation adversely affects the process of intrauterine development of the child.
Occlusion of the blood uteroplacental vessels contributes to the development of persistent fetal hypoxia. If this situation lasts long enough, then this can lead to the development of various anomalies and defects of the intrauterine development.
How to reduce?
To reduce the high level of FDMK in the blood by using various drugs. Appoint them only a doctor. Independent choice and acceptance of these funds can be extremely dangerous for both a pregnant woman and her baby.
The use of such drugs helps not only to normalize hemostasis, but also improves the microcirculation of internal organs. One of the most common drugs is «Heparin». Its introduction allows you to normalize hemostasis and keep the blood in the necessary liquid state.
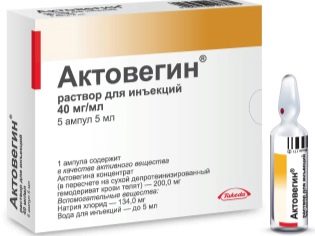
In some cases, doctors prescribe medications aimed at improving microcirculation. These tools include "Curantil" and "Actovegin». These drugs have a positive effect on hemostasis, cause dilated spasm of blood vessels.
In some situations, doctors prescribe folic acid.
Mandatory compliance with the drinking regimen is required to reduce the complex. To do this, expectant mothers should drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day. The best drink is plain water. Expectant mothers with a tendency to edema need to control the amount of fluid consumed.
Improve blood counts can with the help of eating correction. Fresh fruits, vegetables and berries are natural sources of the necessary fluid for the body. Daily use of these products will be an excellent complement to the drinking regime.
In order for the blood to be quite liquid, expectant mothers should carefully control the daily amount of salt consumed, which can also be found in some foods.
Expectant mothers should definitely limit the use of smoked meat, pickles and canned food. Such products contain quite a lot of sodium chloride. For women who have an increased concentration in the blood, FCMK should completely exclude these foods from the daily menu.
For more information on how RFMK is determined during pregnancy and what to do with an increased index, see the following video.